Gingivitis Explained: Maintaining Optimal Gum Health
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease that results in excess plaque and bacteria build up on your teeth causing infection. This may negatively impact your oral health and lead to a series of consequences if not detected and treated on time. The Springfield, VA dentist and their expert team of specialists strive to offer their patients timely diagnosis and treatment for gingivitis.
Read on to learn more about this common dental problem.
A comprehensive guide to gingivitis
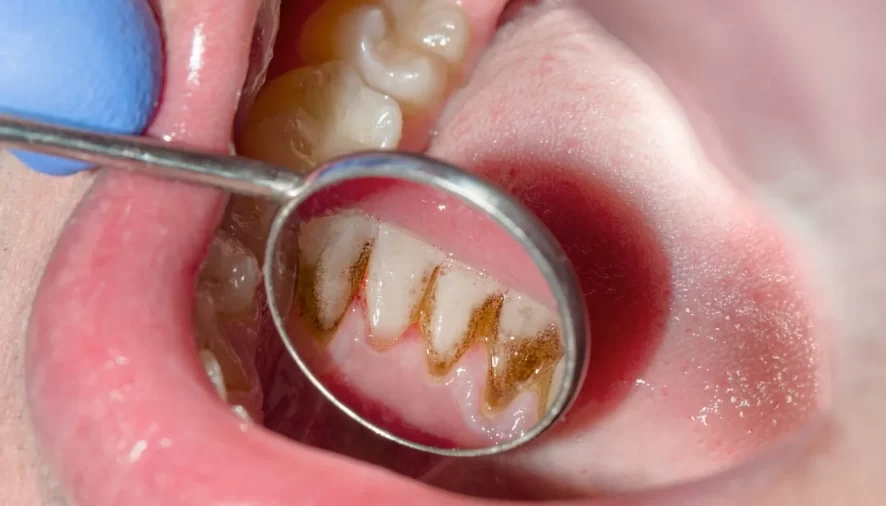
Gingivitis is the earliest form of gum disease that may begin as swollen, red, and bleeding gums. This usually manifests due to increased plaque, tartar, and bacteria buildup, releasing harmful acids that erode the gums. It is a common dental problem wherein almost half of all adults older than 30 develop some form of gum disease.
Potential causes of gingivitis
Gingivitis is most often seen as your body’s inflammatory response to plaque and tartar on your teeth. The acids and toxins released as by-products may irritate your gums and erode them if not treated on time.
Risk factors:
- Diabetes
- Being pregnant
- Having a family history of gum disease
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Consuming alcohol
- Having poor oral hygiene habits
Possible symptoms of gingivitis
You may not notice any symptoms in the initial stage of gingivitis, however, as the condition worsens you may develop:
- Red, swollen, inflamed gums
- Tender, sore, and painful gums
- Bad breath
- Bleeding gums
- Increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- Increased chunks of calculus, especially in your lower teeth
Diagnosing gingivitis
If you have gingivitis symptoms consult your dentist for further evaluation. Your dentist will clinically inspect your oral cavity for:
- Extent of bleeding
- Signs of gum infection like inflammation
- Gum recession
- Loose teeth
X-rays may be required to assess the jawbone involvement, and you might be referred to a periodontist for further management.
Effective treatment modalities for gingivitis
Treatment for gingivitis aims to control the infection and restore healthy teeth and gums.
Treatment options include:
- Scaling
- Supragingival
- Subgingival
- Root planing
- Antimicrobial mouthwash
- Gum grafts and bone grafting for severe cases
Can you prevent gingivitis?
You can prevent the development of gingivitis through the following tips:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly twice daily
- Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Manage diabetes
- Do not smoke or chew tobacco
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Limit foods and drinks with excess sugar content
- Visit a dentist at least once a year for checkups
Your oral cavity consists of both good and bad bacteria. When disease-causing bacteria increase in quantity it leads to infection. This may cause gum inflammation known as gingivitis. Good oral hygiene can stop bacteria from causing gingivitis. Know the early signs of the condition to seek dental help at the right time to prevent further deterioration.