What are Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatments?
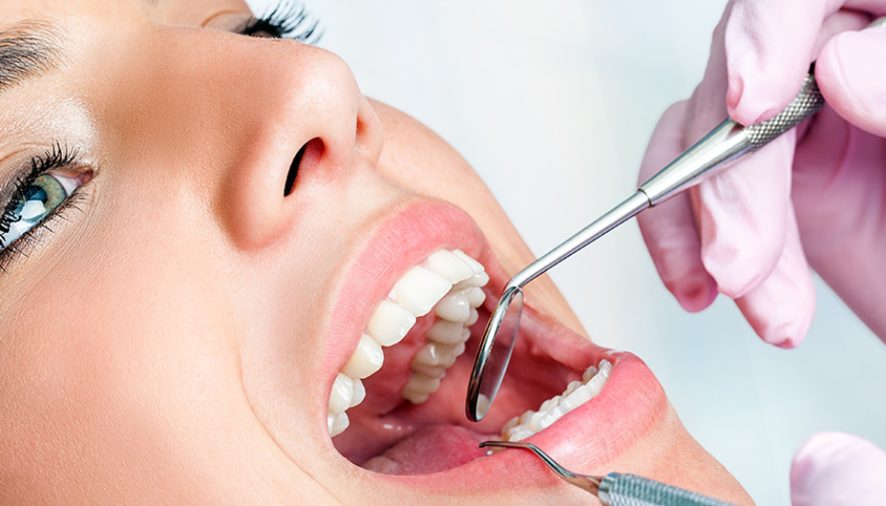
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common dental disorder affecting millions of people worldwide. The disease is responsible for tooth loss and other dental structures, making it a common concern in the dental field, as explained by a Valley Village dentist. Although certain cases necessitate surgical intervention, most forms of gum disease can be treated effectively using non-surgical measures. In this blog post, we shall explore non-surgical periodontal treatment types, the impact and importance of gum restoration, and the prevention of further disease advancement.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the teeth’ surrounding structures. The illness, caused by plaque and tartar leads to gingivitis, which gradually advances to periodontitis. It is a chronic inflammatory condition that occurs in gums and bones progressively due to worsened inflammation. Non-treatment of the disease leads to tooth mobility and progressive loss of the tooth.
Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatments:
Non-surgical approaches are first-life remedies to gum disease. These are designed to smear away tartar and plaque, minimize inflammation, and alleviate gingival tissues.
Scaling and Root Planing: Scaling and root planing are conducted through a technique referred to as deep cleaning. This is done by a dentist or periodontist to eliminate plaque, tartar, and bacteria from under the gum line.
Antimicrobial therapy: After scaling and root planing, the doctor may implement antimicrobial therapy to aid in the elimination of the bacteria that brought about gum disease and helping in ending the recession. The necessary form of antimicrobial therapy may be implemented through chlorhexidine mouthwash or locally applied antibiotics.
Laser therapy: Laser surgery is an effective, safe, and unique non-surgical treatment for gum disease. A dental surgeon may use a dental laser to remove diseased gum tissue and bacteria from a patient’s periodontal pockets. Laser therapy is less invasive than going for standard surgery, and patients usually have less pain and quicker turnaround periods.
Oral hygiene education: To guarantee that gum disease is treated and prevented, it is critical that modified and personalized oral hygiene be done. Patients who have been treated for gum disease need to be instructed on the value of brushing twice per day and flossing as well.
In conclusion, non-surgical periodontal treatments are definitively effective against mild to moderate gum disease. By eliminating plaque and tartar, decreasing inflammation, and boosting gum healing, these procedures can be a fundamental method in reversing gum health and keeping it from deteriorating further. Get in touch with your dentist or periodontist if you have any signs and symptoms. This will allow them to conduct disorder and suggest a one-of-a-kind treatment that is suited exactly to your requirements. If your gum is well taken care of and treated, expect healthy gums to last a lifetime.